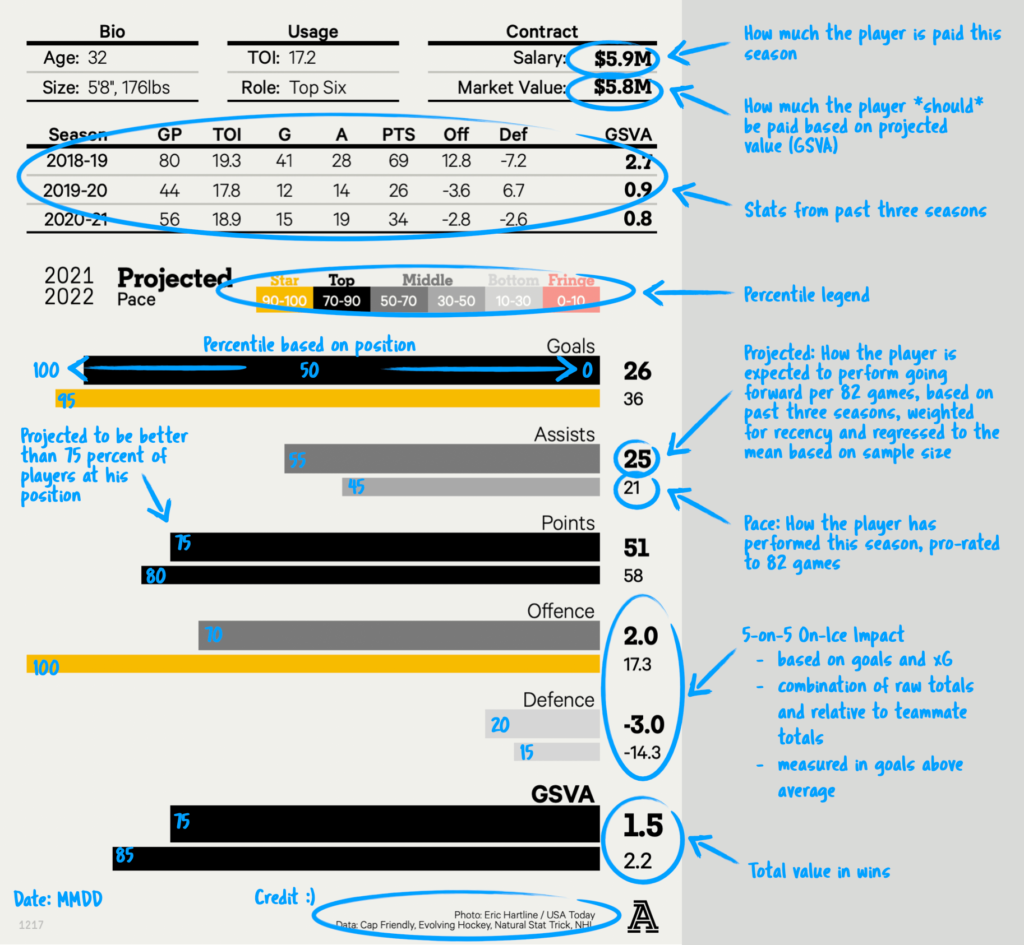
To read a hockey box score, focus on the key statistics: goals, assists, and penalties. Each player’s performance is detailed in individual columns.
Understanding a hockey box score is essential for grasping the game’s dynamics. It breaks down the performance of each player and team. A typical box score includes goals, assists, shots on goal, and penalty minutes. It may also feature faceoff wins, blocked shots, and hits.
The score provides a snapshot of the game’s progression, showing which periods the goals were scored in. Goalie statistics, like saves and save percentage, are also included. This helps fans and analysts evaluate player effectiveness and team strategy. By mastering the box score, you can gain deeper insights into hockey games.

Credit: www.1stohiobattery.com
Introduction To Hockey Box Scores
Understanding hockey box scores helps fans follow the game better. Box scores provide a snapshot of the game’s key moments. They show player performance, goals, assists, and penalties. This guide will help you read and understand these box scores.
Importance Of Box Scores
Box scores are essential for hockey fans and analysts. They offer a quick summary of the game’s events. Coaches use them to evaluate player performance. Fans check them to see how their favorite players performed. Box scores are also useful for fantasy hockey participants.
Basic Components
Box scores contain several important elements:
- Teams: Names of the teams playing.
- Score: Final scores of each team.
- Periods: Goals scored in each period.
- Shots on Goal: Number of shots each team took.
- Power Plays: Number of power play opportunities and goals.
- Penalties: List of penalties, including player and infraction.
Here is a simple table to help you understand:
| Team | Score | 1st Period | 2nd Period | 3rd Period | Shots on Goal | Power Plays |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Team A | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 30 | 1/5 |
| Team B | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 25 | 0/4 |
Each row in the table represents a team. Columns show different aspects of the game. The box score gives a clear view of how the game unfolded.

Credit: hockey-graphs.com
Teams And Players
Reading a hockey box score can seem tricky. But it gets easier if you know what to look for. The “Teams and Players” section is essential. It tells you which teams played and who the players are. Let’s break it down step by step.
Team Listings
The first thing you will see is the team names. These are usually at the top of the box score. Each team has its own column. This layout helps you compare both teams easily.
| Team | Goals | Shots | Penalty Minutes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Team A | 3 | 25 | 10 |
| Team B | 2 | 30 | 8 |
Player Names And Positions
Next, you will see the player names and their positions. This info is usually found under each team’s column. Each player has a row listing their stats.
- Goalie – The player who defends the goal.
- Forward – Players who focus on offense.
- Defense – Players who focus on defense.
Here’s an example layout for players:
| Player Name | Position | Goals | Assists |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Doe | Forward | 1 | 2 |
| Jane Smith | Defense | 0 | 1 |
Individual Player Stats
Understanding individual player stats in a hockey box score is crucial. These stats tell you how each player performed. They also provide insights into the game’s flow. Let’s break down the key stats you’ll see.
Goals And Assists
Goals and assists are the main stats for any player. A goal is scored when the player gets the puck into the net. An assist is given to players who helped make that goal happen.
- Goals: The number of times a player scores in a game.
- Assists: The number of times a player helps score a goal.
For example, if a player scores 2 goals and has 1 assist, it shows they were actively contributing to the team’s offense.
Plus/minus Rating
The plus/minus rating is another key stat. It shows the impact a player has on the game while on the ice.
- Plus: Given when a player is on the ice for a goal scored by their team.
- Minus: Given when a player is on the ice for a goal scored by the opposing team.
For instance, if a player has a +2 rating, it means they were on the ice for two more goals by their team than by the opponent.
Here’s a quick look at how these stats might appear in a box score:
| Player | Goals | Assists | Plus/Minus |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Doe | 2 | 1 | +2 |
| Jane Smith | 0 | 3 | -1 |
By looking at these stats, you can easily see which players had a big impact on the game.
Goaltender Statistics
Understanding goaltender statistics is crucial for hockey fans. It helps you evaluate a goalie’s performance. This section will break down key stats. Let’s dive into the numbers that matter.
Saves And Shots Faced
The saves stat shows how many shots a goalie stopped. It’s a key measure of their skill. A higher number means better performance. The shots faced stat tells how many shots the goalie faced. This helps you understand the pressure they were under.
Here’s a table to illustrate:
| Game | Saves | Shots Faced |
|---|---|---|
| Game 1 | 25 | 30 |
| Game 2 | 30 | 35 |
Use these stats to gauge a goalie’s effectiveness. Both numbers are important. They tell a story together. High saves with high shots faced indicate a strong performance.
Goals Against Average
The Goals Against Average (GAA) is another key stat. It shows the average goals a goalie allows per game. A lower GAA means better performance. It’s calculated by dividing goals allowed by games played.
GAA = (Goals Allowed / Games Played)Here’s an example:
| Games Played | Goals Allowed | GAA |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 2.00 |
| 15 | 30 | 2.00 |
Low GAA is a sign of a great goalie. Compare GAA across games to see trends. Use GAA to assess long-term performance. It’s a reliable metric for evaluating goalies.
Special Teams Performance
Understanding special teams performance is crucial in reading a hockey box score. This section focuses on two key metrics: power play success and penalty kill efficiency. These metrics can influence the outcome of a game significantly.
Power Play Success
Power play success measures a team’s effectiveness during power plays. A power play occurs when the opponent has a player in the penalty box. This gives the team a one-player advantage. The box score displays the number of power play opportunities and the number of goals scored.
| Team | Power Play Opportunities | Power Play Goals | Power Play Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Team A | 5 | 2 | 40% |
| Team B | 3 | 1 | 33.3% |
Penalty Kill Efficiency
Penalty kill efficiency shows how well a team defends against power plays. It is measured by the percentage of successful penalty kills. A successful penalty kill means the team did not allow a goal while having fewer players on the ice.
- Count the number of penalty kills.
- Note the number of goals allowed during these kills.
- Calculate the efficiency percentage.
Penalty Kill Efficiency = (Successful Penalty Kills / Total Penalty Kills) 100For example, if a team faced 4 power plays and allowed 1 goal, the efficiency is 75%.
Credit: hockeyanswered.com
Advanced Metrics
Advanced metrics offer deeper insights into hockey performance. These metrics go beyond the basics. They help you understand a player’s true impact. Here, we will focus on two key advanced metrics: Corsi and Fenwick and Expected Goals.
Corsi And Fenwick
Corsi measures shot attempts. It includes shots on goal, missed shots, and blocked shots. This metric helps gauge puck possession. The more shot attempts a team has, the more they control the game.
| Metric | Includes |
|---|---|
| Corsi | Shots on goal, missed shots, blocked shots |
Fenwick is similar to Corsi but excludes blocked shots. This metric focuses on unblocked shot attempts. It provides a clearer picture of a team’s offensive performance.
| Metric | Excludes |
|---|---|
| Fenwick | Blocked shots |
Expected Goals
Expected Goals (xG) predict the likelihood of a shot becoming a goal. This metric considers shot quality and location. It helps evaluate scoring chances more accurately.
Factors that influence xG include:
- Shot distance
- Shot angle
- Type of shot
Teams with higher xG are creating better scoring opportunities. This metric is useful for both teams and individual players.
Understanding these advanced metrics can improve your analysis of hockey games. They provide valuable insights into team and player performances.
Interpreting Trends
Reading a hockey box score is not just about numbers. It reveals patterns and trends. These trends help you understand player performances and team dynamics. In this section, we will break down how to interpret these trends.
Identifying Patterns
Patterns in a box score can tell a story. Look at the goals, assists, and penalty minutes. Are there players who consistently score? Do some players get more penalties? These insights help you see which players are performing well.
- Consistent scorers are key players.
- High penalty minutes can affect team performance.
Another pattern to watch is shots on goal. Players with many shots are usually active and involved. This can indicate future scoring opportunities.
| Player | Goals | Assists | Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Player A | 5 | 7 | 2 |
| Player B | 3 | 5 | 8 |
Using Stats For Predictions
Statistics can help predict future outcomes. If a player has many goals and assists, they are likely to continue performing well. Look at the team’s win/loss record. A team with a strong record is likely to keep winning.
- Review player performance over multiple games.
- Check team records and trends.
Goalie stats are also crucial. A goalie with a high save percentage is reliable. This can affect the team’s chances of winning.
| Goalie | Save Percentage | Wins | Losses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goalie A | .920 | 15 | 5 |
| Goalie B | .850 | 8 | 12 |
Use these stats to make informed predictions. Predicting trends can enhance your understanding of the game.
Conclusion
Mastering how to read a hockey box score enhances your game-watching experience. It provides valuable insights into player performances. Now, you can better analyze statistics and understand the game’s flow. Keep practicing, and soon, you’ll read box scores with ease.
Enjoy your deeper connection to the sport of hockey!